How big is that risk in our nation? Check out the following map of nations with the most and least privacy protections for their citizens. Guess who is on the bottom? Yep, you guessed it. The good ole US of A.

CLICK MAP TO ENLARGE
Summary of Findings
No right to privacy in constitution, though search and seizure protections exist in 4th Amendment; case law on government searches has considered new technology
No comprehensive privacy law, many sectoral laws; though tort of privacy
FTC continues to give inadequate attention to privacy issues, though issued self-regulating privacy guidelines on advertising in 2007
State-level data breach legislation has proven to be useful in identifying faults in security
REAL-ID and biometric identification programs continue to spread without adequate oversight, research, and funding structures
Extensive data-sharing programs across federal government and with private sector
Spreading use of CCTV
Congress approved presidential program of spying on foreign communications over U.S. networks, e.g. Gmail, Hotmail, etc.; and now considering immunity for telephone companies, while government claims secrecy, thus barring any legal action
No data retention law as yet, but equally no data protection law
World leading in border surveillance, mandating trans-border data flows
Weak protections of financial and medical privacy; plans spread for 'rings of steel' around cities to monitor movements of individuals
Democratic safeguards tend to be strong but new Congress and political dynamics show that immigration and terrorism continue to leave politicians scared and without principle
Lack of action on data breach legislation on the federal level while REAL-ID is still compelled upon states has shown that states can make informed decisions
Recent news regarding FBI biometric database raises particular concerns as this could lead to the largest database of biometrics around the world that is not protected by strong privacy law
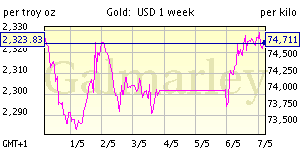
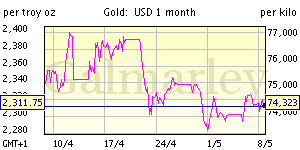
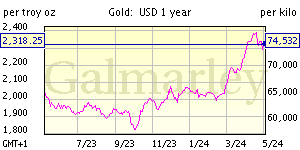
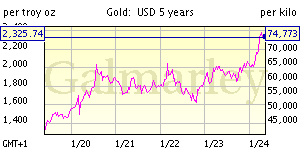
![[Most Recent Quotes from www.kitco.com]](http://www.kitconet.com/images/quotes_7a.gif)